This post continues my interview with Torsten Moses about BLADE, the new LISP IDE that arrived with BricsCAD V18.2. See here for post 1.
Steve: I’ve noted before that BricsCAD execution of AutoLISP and Visual LISP is several times faster than AutoCAD’s. How does the new technology affect that performance?
Torsten: All the new BLADE-related stuff doesn’t really affect normal LISP execution outside the IDE and debugger. The connection is made by a few callbacks, which take zero time in normal processing. Therefore there is also no chance of breaking things. The BLADE implementation is very safe, and performance remains high for normal usage. For the debugger and the synchronization, it is all home-brewed stuff, optimized for best performance even when debugging, and minimum system and LISP memory usage.
In the course of implementing the debugger and internal versus external synchronization, I also removed most emulations and implemented that as core OpenLisp functionality. That has the side-effect that the (repeat), (foreach) and (vlax-for) functions now run about five times faster at the loop construction. So rather than slowing things down, creating BLADE has actually speeded things up!
Steve: Will the Mac and Linux versions also get this feature?
Torsten: Yes, it is fully compatible. This is due to the implementations of WxWidgets and my own stuff. I have already verified BLADE running under Linux. There are no differences; even the implementation code has no Windows-specific stuff.
Steve: Can you give a simple example of the workflow of a debugging session?
Torsten: First, don’t pre-load any LISP file into BricsCAD. Such code loaded outside the debugger is fully functional, but it can’t be used for debugging. The special connection between internal and external representation is only established when loading the LISP code under a debug state.
Next, in BLADE open an existing FAS or VLX project, and/or a “Named Session”, or simply any LISP file you want to start debugging with.
Now you can select Start Debugging from menu or toolbar, or hit the F8 hotkey. The special Debug Toolbar will appear. You can either activate AutoBreak, which stops at first executable code, or activate the LISP source where you want to start debugging and place some breakpoints.
Then load the dedicated LISP file, either by the normal Load into BricsCAD function, or from the Load button in the Debug Toolbar. Now that loaded code is debug-enabled and you will see the file and debug-enabled functions in the two right tabs.
When the debugger halts at the first breakpoint, all debug-step modes are enabled in the toolbar, and you have all the usual debug step modes. More than in AutoCAD’s VLIDE, actually. You can set the watches (observed and tracked variables) as “Data Break Point” by activating the checkbox. Then, whenever that value changes, the debugger also stops automatically at the related LISP statement.
Steve: What if your code calls code in other files you haven’t loaded?
Torsten: Don’t worry about that. The debugger recognizes this and will ask to load the related LISP file on-demand. In normal LISP, you would get an unknown function error but the debugger catches this upfront. In fact, this is one of the high-end features – only load the primary LISP file, any further debugging into other files resolves by loading during the debugging session. This is very handy for dealing with complex apps – there’s no need to preload any other LISP source. I’m sure you’ve experienced Murphy’s Law, where the particular function you need is the one that’s not loaded. You won’t have that problem in BLADE.
Steve: Where to from here? Is this job done or is there still room for improvement?
Torsten: As BLADE is still a very young product, there is definitely a lot more to come. So far, the main target was to provide good debugging features, and a somewhat reasonable handling of projects, but not so much focusing on plain editor capabilities.
My to-do list still has a number of major key features to be implemented. We want to add a hotkey editor, because every developer loves his own keystrokes and learning others is a nightmare! We also want cross-reference checking on a per-file and per-session basis, mainly for bigger LISP applications.
Then, over time, the editor capabilities will be extended and improved, providing more features. One example is to provide an editor tooltip that shows a function signature and short help when hovering over a LISP function name.
And of course, I’m aware that when people start using this in production, a lot of feedback will arrive from developers in the form of wishes, hints for improvements and bug reports. It’s very likely there will be many wishes to implement several details to make BLADE resemble AutoCAD’s VLIDE more closely. This could be a bit difficult sometimes, and is also not the main target. I hope that developers will be open to a slightly different workflow, given the big advantages they get in return.
In general we are very open to developer ideas, needs and requirements, as we are with BricsCAD itself. In the end, it’s the developer who needs to work with BLADE, as easily and productively as possible. Even the initial release of BLADE is based on important feedback from beta testers such as Martin Drese (CAD Wiesel).
Steve: I can certainly attest to how well you respond to feedback. I’ve seen bugs I’ve reported fixed in a very short timeframe.
Torsten, thank you for your time. This has been very illuminating.
This interview is also available in one post on the Bricsys blog.


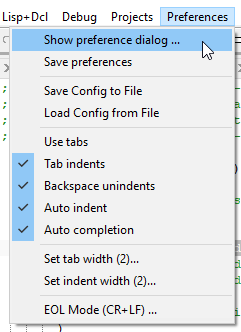
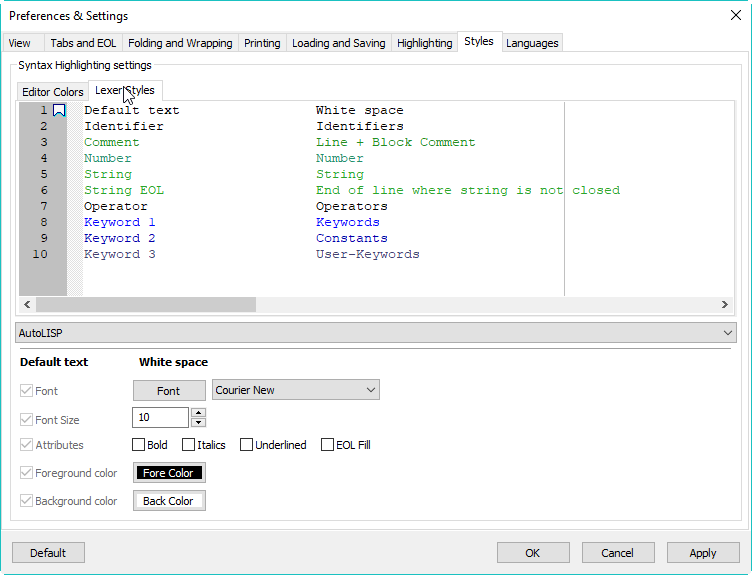
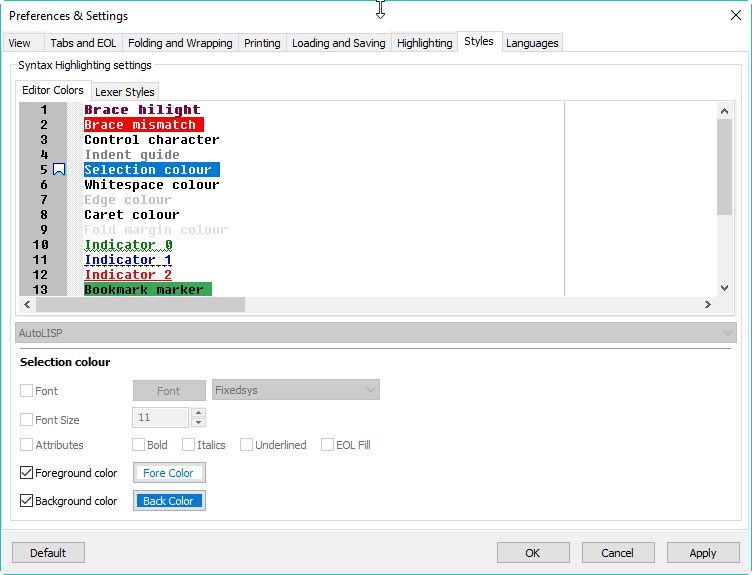
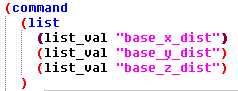
 There are several things in the above image that might be unfamiliar but which I suggest you leave turned on because they’re useful. If you really insist, here are the locations for these settings in the Preferences & Settings dialog:
There are several things in the above image that might be unfamiliar but which I suggest you leave turned on because they’re useful. If you really insist, here are the locations for these settings in the Preferences & Settings dialog: